Irrigation in Greenhouses
02 April 2024 Tuesday
Irrigation in Greenhouses
IRRIGATION IN GREENHOUSES
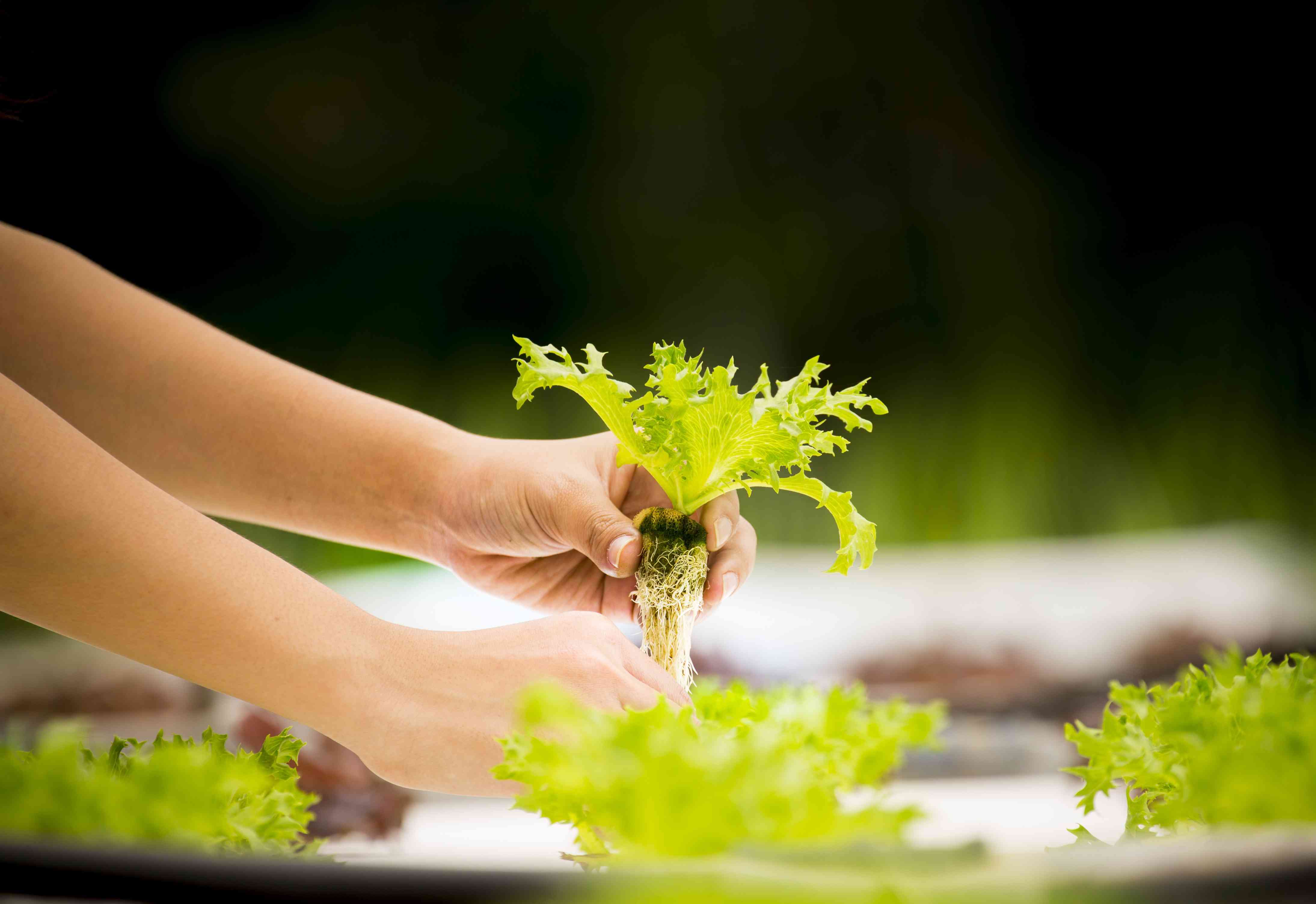
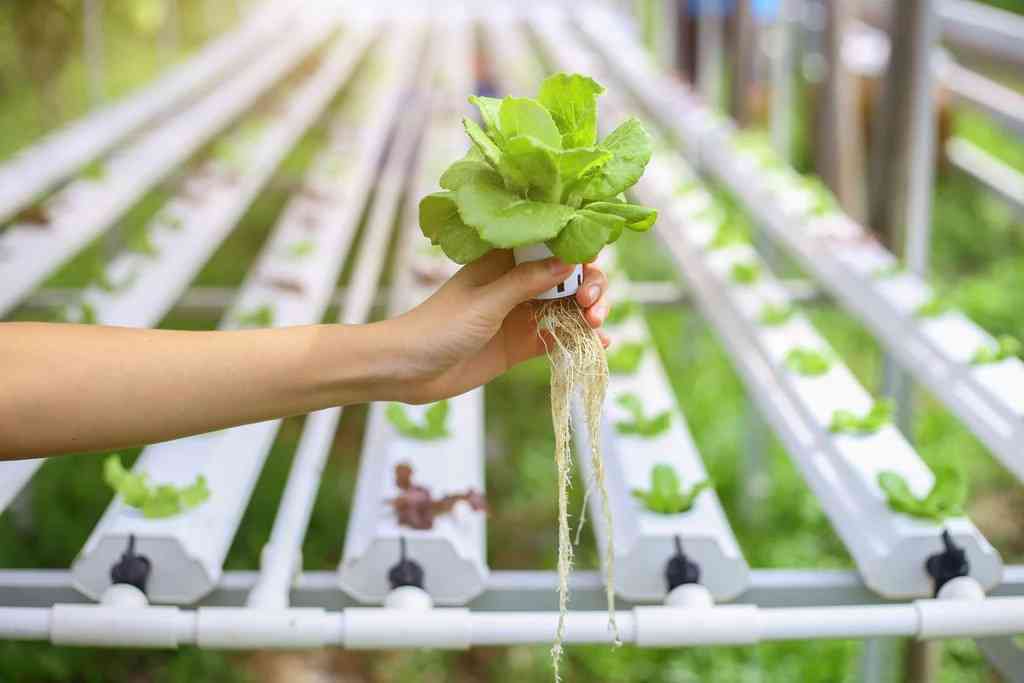
Irrigation is generally defined as the delivery of water to the plant root area by various methods, which the plant cannot receive through natural rainfall. Irrigation in the greenhouse is the delivery of water required for plant growth to the soil through various systems. In order to provide good irrigation, it is first necessary to choose an irrigation method according to the characteristics of the plant and the soil. Then, it is necessary to know when, how much and how to give water.
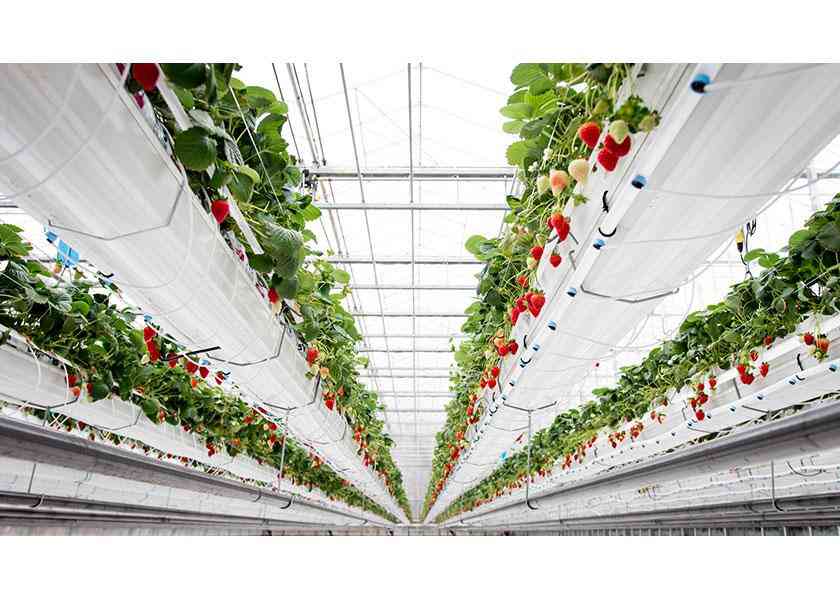
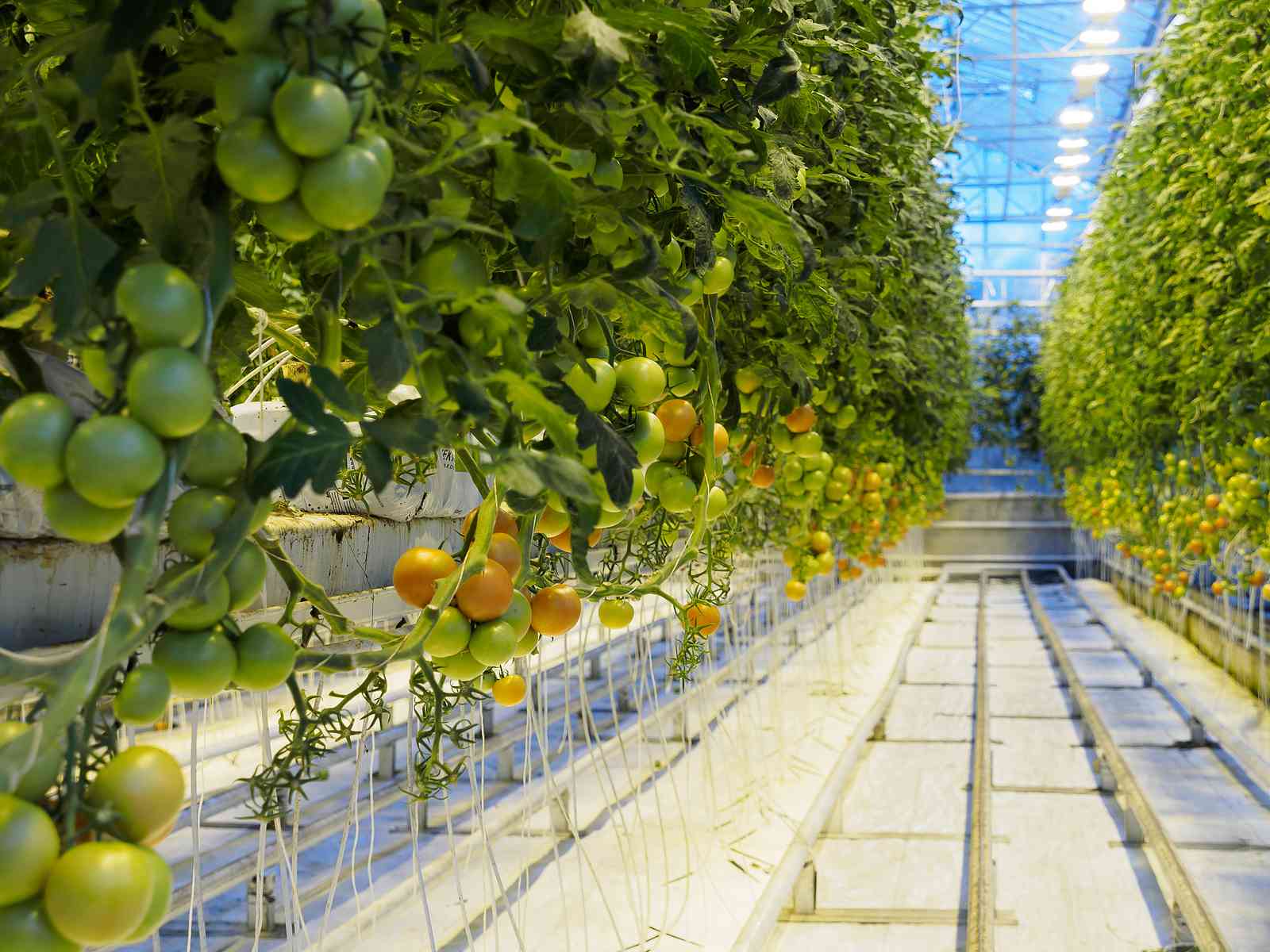
✓Irrigation Systems Used in Greenhouses
✓Irrigation with Strainer Bucket and Hose
✓Surface Irrigation System
✓Sprinkler Irrigation System
✓Drip Irrigation System
✓Irrigation system made with perforated pipes
✓Subground irrigation system
✓Sand culture irrigation systems
✓Capillary irrigation system
- Irrigation with a Filter Bucket and Hose = Buckets with a strainer and hoses with different types of sprayers or strainers at the ends, used for small-scale irrigation in gardens, gardens and greenhouses, can be considered as simple sprinklers.
-Surface Irrigation System= Controlling the distribution of applied water by the soil surface, requiring preliminary preparation of the land for irrigation, and requiring an effective water distribution system. Surface irrigation methods applied in greenhouses provide an advantage over other methods in that they can irrigate a large surface in a short time. In addition, surface irrigation systems require lower operating costs compared to other methods because they require lower energy. Surface irrigation system is divided into two: pan irrigation and furrow irrigation.
-Sprinkler Irrigation System= Sprinkler irrigation system is a network consisting of pipes with nozzles that spray water on the soil surface in the form of fine droplets under a certain pressure. In the sprinkler irrigation method, water is sprayed from rotating or fixed sprinkler heads under a certain pressure and delivered to the plant or soil surface.
-Drip Irrigation System = Drip irrigation method is a method in which purified water and fertilizer are dripped onto the soil surface under low pressure at short intervals of time. In this method, water can be carried to each plant through a widespread pipe network. Drippers reduce the pressure in the pipe network through a small orifice or a long flow path, allowing it to flow at a small flow rate of a few liters per hour. The elements that make up a drip system can be classified as pump and power unit, filter system, piping system and drippers.
-Irrigation System Made with Perforated Pipes= In this irrigation system, water is delivered to the plants with the help of holes opened at approximately 7 cm intervals on both sides of the polyethylene pipes. One end of the pipe used is closed with a blind plug and a connection is made with the main distribution pipe from the other end. When water is supplied to the system, the water in the pipes, which swell under pressure and take a cylindrical shape, comes out of the holes in small jets. Although the system is quite economical, it requires more attention in application.
-Subsoil Irrigation System = In this method, water is delivered directly to the plant root area through perforated pipes laid underground. Since there is no water in the system that would cause any damage to the soil surface, a crust layer does not form. In this method, evaporation from the soil surface will be minimized and moisture saturation in the greenhouse will be significantly reduced.
-Sand Culture Irrigation System= In addition to the surface and pressurized systems used to irrigate greenhouse plants, sand culture irrigation systems based on capillarity principles and capillary pipe irrigation systems based on the same principle are widely used, especially in greenhouses where cut flower cultivation is carried out.
-Capillary Irrigation System= In these irrigations carried out using very small diameter capillary pipes, the principle that the water given to the laterals under very low pressure rises in the capillary pipes connected to these laterals and reaches the plants in the pots. The diameters of the laterals used for this purpose may vary between 25-35 mm. The diameters of the capillary pipes, which connect to the laterals and provide water transmission to the pots, vary between 1.25-1.50 mm.









What are you waiting for a profitable investment?
Call Us Now!
444 2 548