Geothermal Greenhouse

02 April 2024 Tuesday
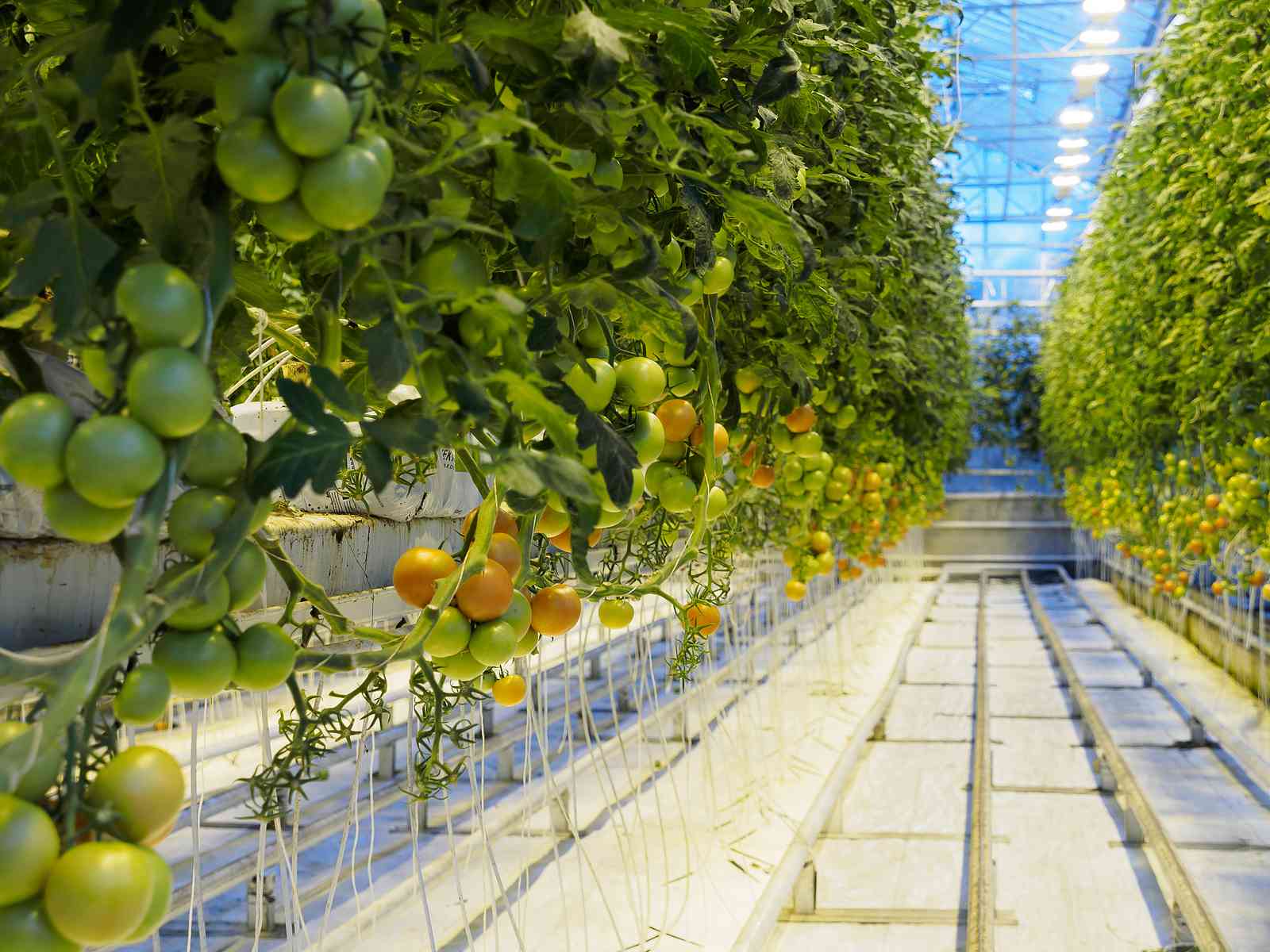
Geothermal Greenhouse
Why Geothermal Soilless Greenhouse?
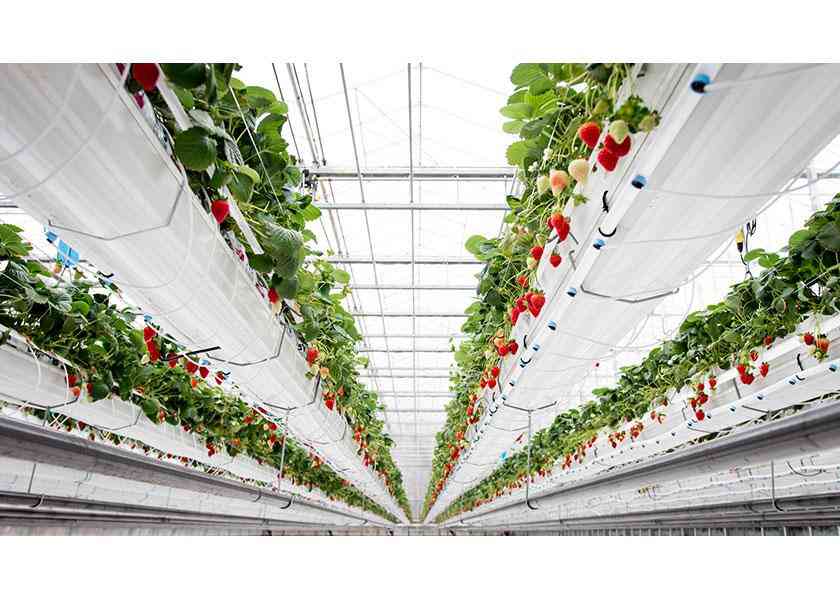
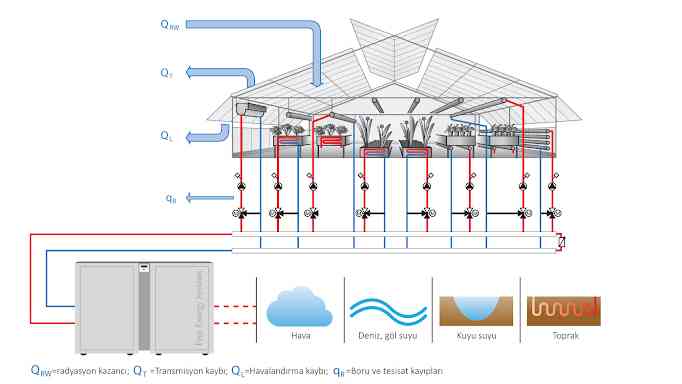
In modern greenhouses where soilless culture is carried out, production can be made throughout the year by providing adequate heating, lighting, ventilation and carbon dioxide requirements of the plant to be grown. However, especially heating constitutes the most important cost element and has a limiting effect. In addition to fossil fuels (fueloil, LPG, coal, natural gas, etc.), renewable energy sources (solar energy, geothermal energy, biomass, etc.) are also used as energy sources in greenhouse heating. Among fossil fuels, the use of high-quality coal is economical, but the heating cost decreases even more in regions where geothermal hot water resources are located. The use of geothermal energy in agricultural production areas not only provides the warmth needed by the plant, but also allows production to be carried out at any time of the year without interruption, except for extremely hot periods. In greenhouses where heating is done regularly, the risk of disease, as well as product quality, is minimized.
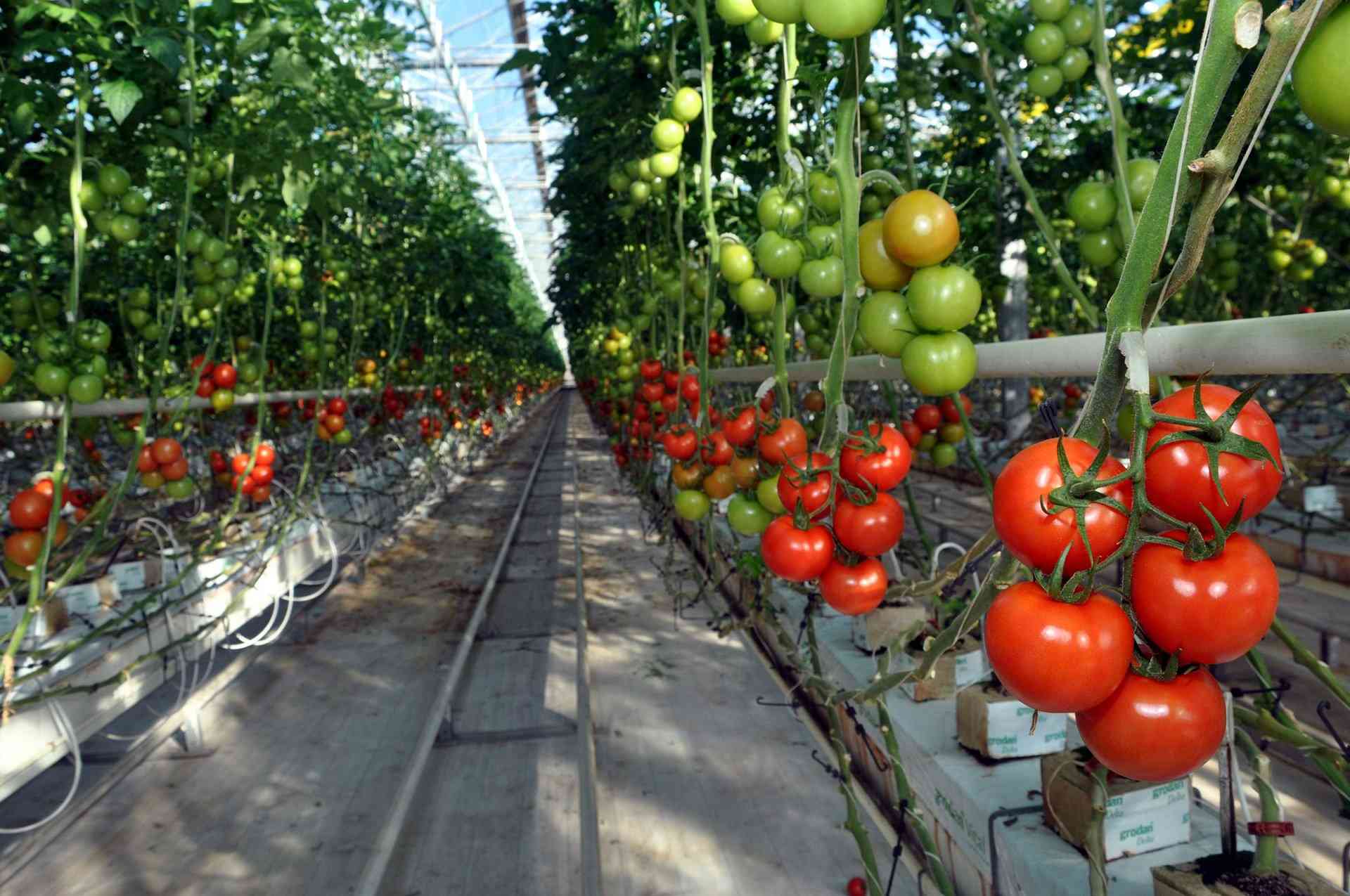
How to Make a Geothermal Soilless Greenhouse.
It is mixed with hot water from geothermal wells (temperature of the water is 75-80°C) and given to the greenhouses. On days when the temperature increases, the temperature of the water supplied to the greenhouses is further reduced and ventilation is opened. Ventilation also allows the carbon dioxide necessary for the plants to enter the greenhouse. Steel insulated pipes laid inside the greenhouses are used for heating. Most heating is done in the winter season when average temperatures are lowest. Although some greenhouses have thermometers, the heating system is not indexed to the thermometer measurement in the greenhouses. The purpose is not only to protect the plant from frost, but also to provide the necessary warmth for the plant to continue its development. However, the heating in our country's greenhouses is mostly done not to provide the optimum temperature desired by the plants, but to prevent them from being damaged by frost. The reason for this is the high heating costs. Keeping the temperature below 10-12°C for several days in a row negatively affects productivity and quality.
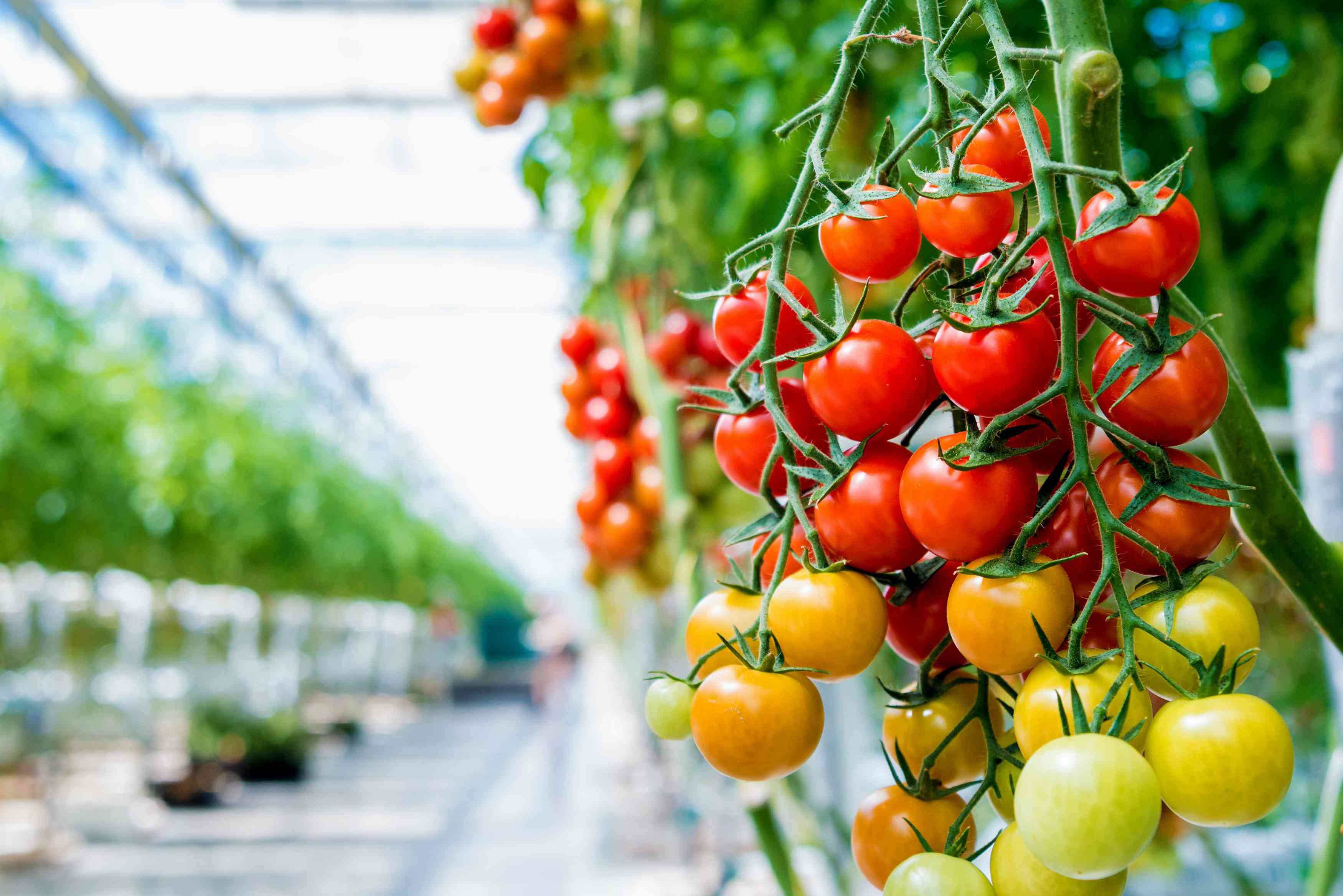








What are you waiting for a profitable investment?
Call Us Now!
444 2 548